With the continuous development of gas turbines and aero-engines, the gas temperature in front of the turbine is getting higher and higher, and the requirements for high-temperature strength of high-temperature alloys are getting higher and higher. Therefore, the degree of alloying of turbine blade materials is increasing, and the number of reinforcing phases is increasing. High temperature alloys for turbine blades have gone through a development process from deformed high temperature alloys to equiaxial crystal casting alloys to directionally solidified column crystal and single crystal high temperature alloys. This chapter will focus on the composition, organization and properties of high temperature alloys for turbine blades at home and abroad.
Deformation of high-temperature alloy for turbine blades
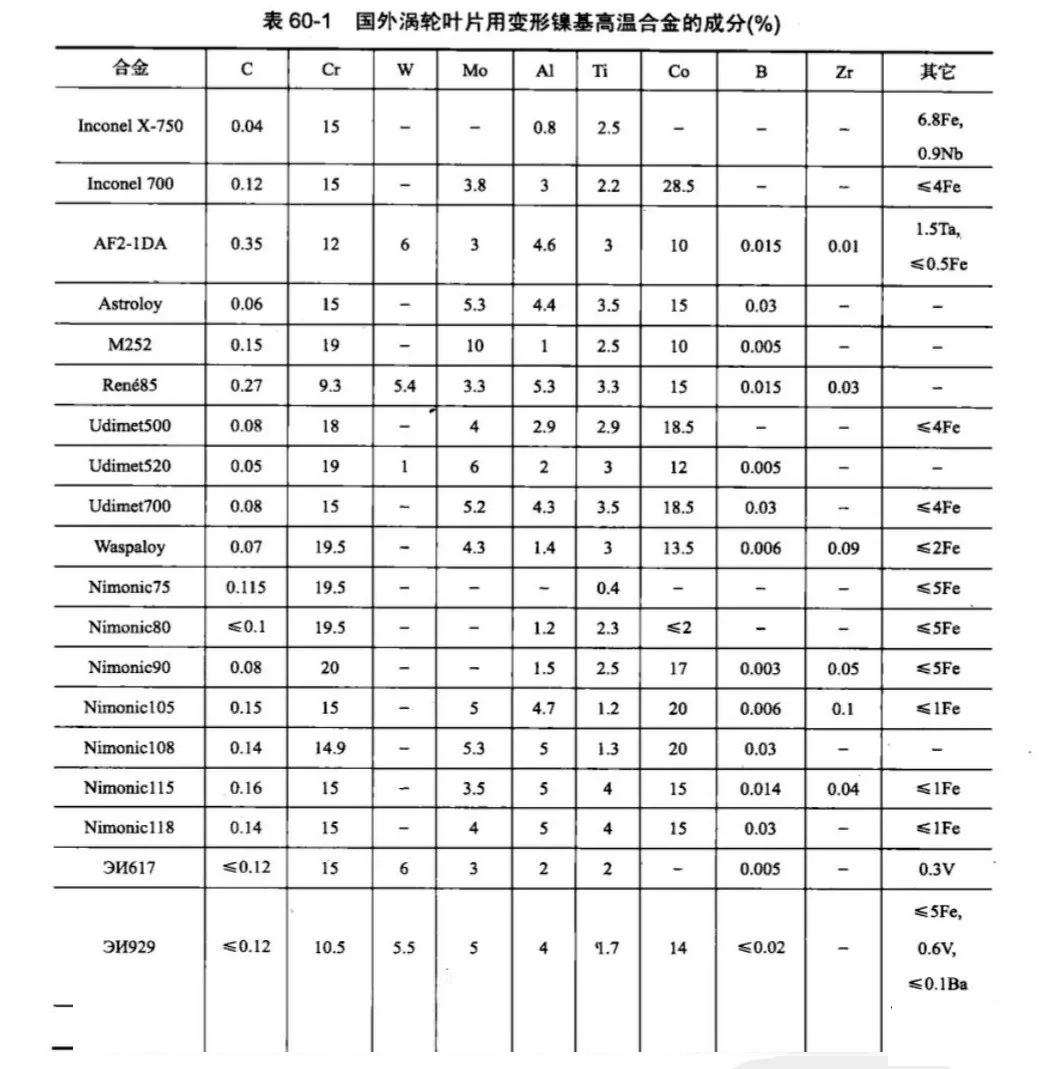
Domestic and foreign turbine blade with deformation of the composition of high-temperature alloys
1. Foreign turbine blade with deformation of high-temperature alloy composition of foreign turbine blade with nickel-based deformation of most of the high-temperature alloys contain 15% ~ 20% of Cr for solid solution strengthening, the formation of Ni-Cr matrix. At the same time, Cr can also ensure the formation of Cr2O3-based oxide film, so that the alloy has sufficient oxidation and thermal corrosion resistance. The earliest deformed high-temperature alloys, Nimonic75, Nimonic80 and Inconelx-750, were developed on this principle. In order to further improve the strength, the addition of 10% ~ 20% of Co, reduce the matrix stacking layer wrong energy, so that the cross-slip shift more difficult, resulting in solid solution strengthening.
Most alloys also add 3% ~ 6% of Mo for solid solution strengthening, a small number of alloys are also added at the same time 1% ~ 6% of W for solid solution strengthening. Solid solution strengthening of the alloy matrix strength has been significantly improved, but not enough to bear the turbine blade at high temperatures and complex stress conditions, therefore, it is also necessary to add Al and Ti for y-phase precipitation strengthening. the higher the content of Al + Ti, the more the number of γ-phase, the better the effect of strengthening, Nb and Ta in addition to dissolve into the y matrix solid solution strengthening, but also a large number of into the γ-phase, strengthen the r-phase, increase the number of y’phase, improve the dissolution temperature of γ phase, and increase the number of γ phase. Improve the dissolution temperature of the γ phase, enhance the effect of y’phase strengthening. Precipitation strengthening of high temperature alloys γ phase strengthening is the main strengthening mechanism. In order to further improve the creep, endurance strength, but also add about 0.005% ~ 0.015% or so of boron, in order to improve the interatomic bonding of grain boundaries, strengthen the grain boundaries, a few alloys also added 0.01% ~ 0.1% of Zr, and B together with the combination of strengthening the grain boundaries. The development of the former Soviet Union turbine blade alloys such as 3N617, 3N929 and 3П220, etc., but also added 0.3% to 0.6% of V, of which 70% to 90% dissolved into the y matrix, play a role in solid solution strengthening, and significantly improve the plasticity of hot working. Table 60-1 gives the composition of foreign turbine blade with deformation of nickel-based high-temperature alloys.
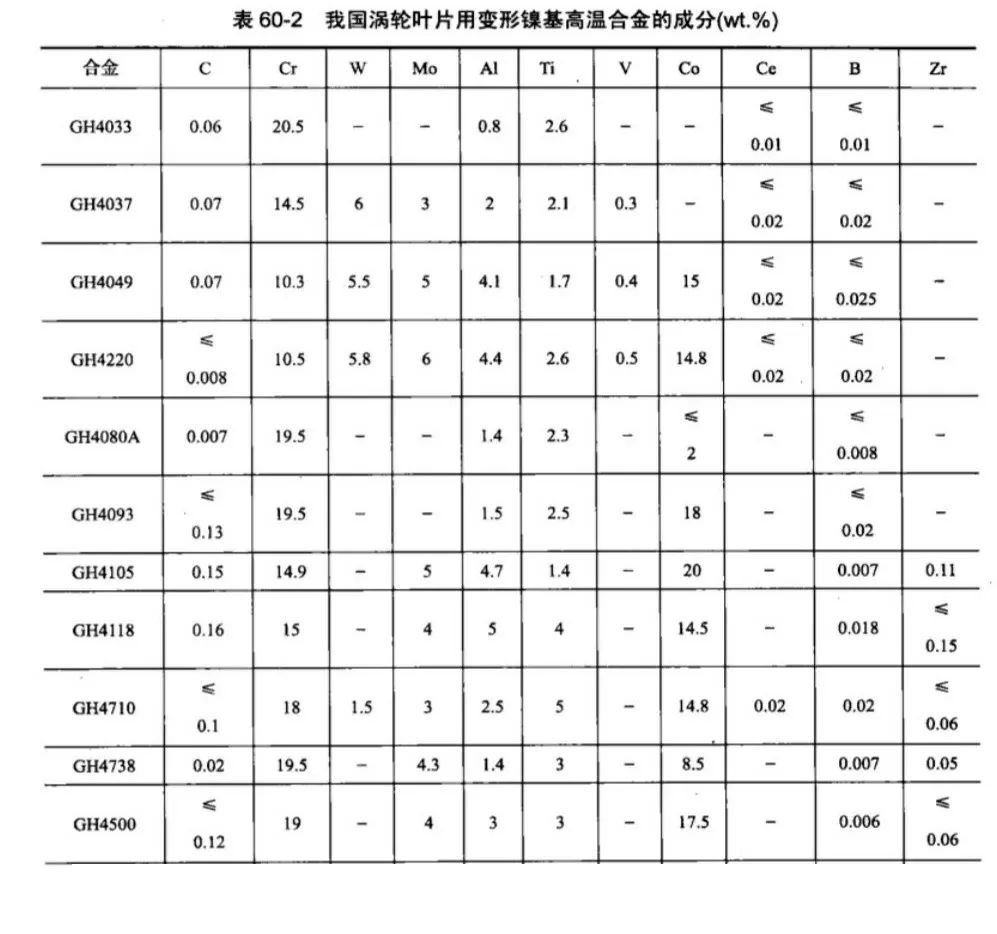
2. Domestic turbine blade with deformation of high-temperature alloy composition of China’s production of nickel-based deformation of high-temperature alloys most of the reference to the corresponding foreign alloy composition on the basis of the successful development. Table 60-2 for the domestic nickel-based deformation of the chemical composition of high-temperature alloys, the role of alloying elements and foreign deformation of high-temperature alloys. GH4413 for the authors equal to 2001 began the development of nickel-based deformation alloy, is a high-strength alloys, adding about 7% of Al and Ti, the formation of about 29% of the spherical γ-phase for precipitation strengthening, 13% of W and Mo for solid solution strengthening, and contains 15% Co and 10.5% Cr as a sufficient strength of the Ni-Cr-Co substrate, and also contains a trace boron to strengthen the grain boundaries. GH4413 is a material for turbine blades for naval gas turbines and is used to make 5th and 6th stage turbine blades.
Post time: Aug-05-2023